Definition:
A function f: ℝ -→ ℝ associates to each number x in its domain exactly one number f(x).
Example 1:
H: ℝ -→ ℝ associates to each number t > 0 the height of a falling object t seconds after it was dropped.
Example 2:
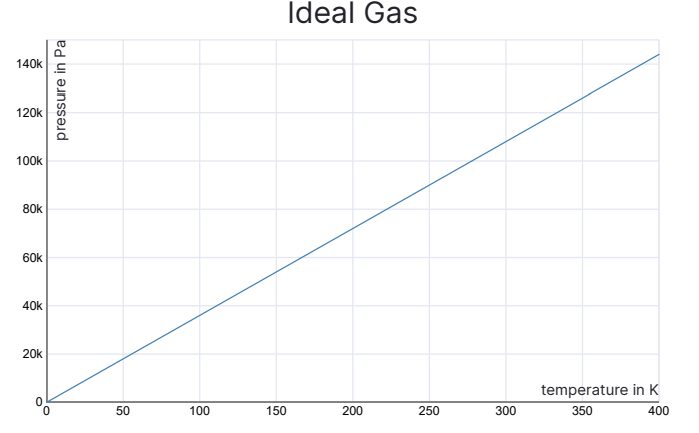
P: ℝ -→ ℝ associates to each number T ≥ 0 the pressure of an ideal gas at temperature T Kelvins.
Falling Object Formula:
So, for m and
Ideal Gas Formula:
Definition:
The graph of a function f: ℝ -→ ℝ is the curve going through all the points (x, f(x)) for x in the domain of f.
Graph Example:
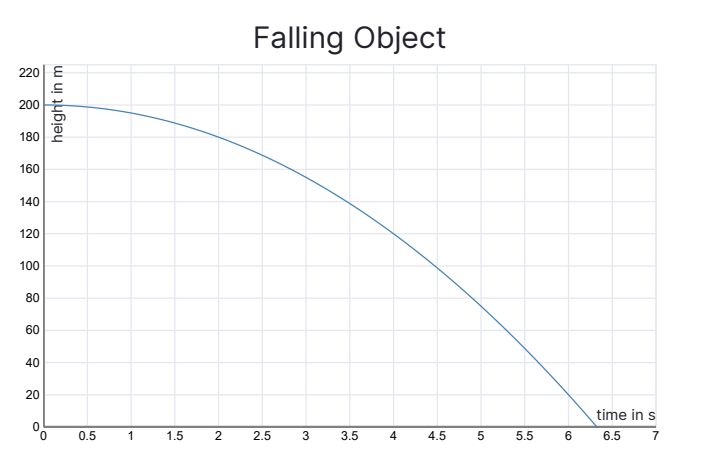
To find values from the graph, you can use a reading off way. For falling object, when t is equal to 5, then the output which is the height will be 75.
To figure out if a graph is a function or not, we use the Vertical Line test.
Theorem
A curve in the plane is the graph of a function over a certain domain if every vertical line at x-values in that domain intersects the curve exactly once.
Example 1:
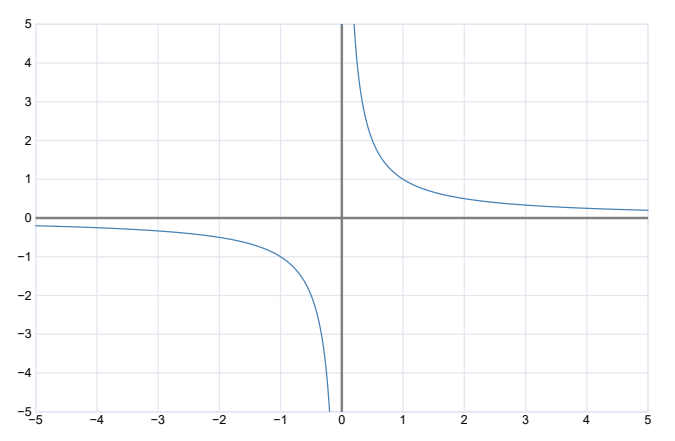
Using the vertical line test, there is only 1 point on each vertical line, therefore making this a function.
Caution
A circle is not a function as it does not pass the Vertical Line test.