Table of Contents
Crystal Structure of Metals
Atomic Radii and Crystal Structures for 16 Metals
| Metal | Crystal Structure | Atomic Radius | Metal | Crystal Structure | Atomic Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | FCC | 0.1431 | Molybdenum | BCC | 0.1363 |
| Cadmium | HCP | 0.1490 | Nickel | FCC | 0.1246 |
| Chromium | BCC | 0.1249 | Platinum | FCC | 0.1387 |
| Cobalt | HCP | 0.1253 | Silver | FCC | 0.1445 |
| Copper | FCC | 0.1278 | Tantalum | BCC | 0.1430 |
| Gold | FCC | 0.1442 | Titanium () | HCP | 0.1445 |
| Iron () | BCC | 0.1241 | Tungsten | BCC | 0.1371 |
| Lead | FCC | 0.1750 | Zinc | HCP | 0.1332 |
FCC = face-centered cubic; HCP = hexagonal close-packed; BCC = body-centered cubic.
A nanometer (nm) equals m; to convert from nanometers to angstrom units (), multiply the nanometer value by 10.
- Number of atoms in a unit cell.
- Coordination number (CN): # of the nearest-neighbor atoms
- Atomic packing factor (APF): vol.% of atoms in a unit cell
Structural Parameters
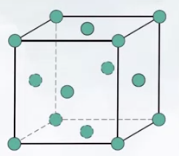
Total Number of Atoms in a Unit Cell (N):
- : atoms inside a unit cell.
- : atoms on the surfaces of a unit cell.
- : atoms at the corners of a unit cell. Atomic Packing Factor (APF):
- Lattice Parameter ⇒
- Atomic Radius ⇒
- Atom Number ⇒ Theoretical Density of a Crystal
- ⇒ number of atoms associated with each unit cell
- ⇒ atomic weight
- ⇒ volume of the unit cell
- ⇒ Avogadro’s number ( atoms/mol)
Solid Solutions
Substitutional Solid Solution:
- the alloying element atoms replace host atoms at the lattice sites
- Using solvent atoms and solute atoms. Interstitial Solid Solution:
- the alloying element atoms occupy the interstitial sites in the host element lattice
Single v.s. Poly-Crystals
Single Crystals: The periodic arrangement of atoms extends throughout the entirety of the specimen without interruption. (Usually characterized by facets)
Polycrystal: The crystal is comprised of a collection of many single crystals (grains, to be elaborated in the next chapter on crystal defects).