school-note Referring to 4 The Inverse Function and Invertibility, there is a test called the horizontal line test. Also shown below:
Theorem
A function is invertible if and only if all horizontal lines intersect the graph of the function in at most 1 place.
If we look at the sine function graph, we can tell that it does not pass the horizontal line test. We can say that therefore, it does not have an inverse function. This may only be true for some circumstances.

This sine graph clearly does not pass the horizontal line test and according to the theorem, it does not have an inverse. Unless, we limit the domain of the function so that it passes the horizontal line test. We can limit the domain to where an inverse of exists.
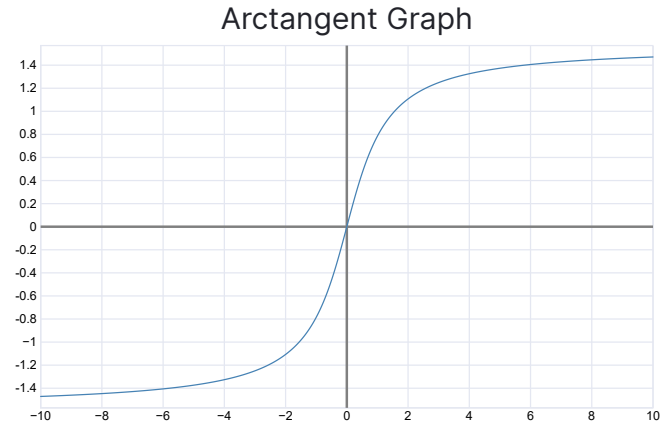
is the inverse of
Definition
The inverse of is the function . Domain: -⇒ Range: is also denoted as
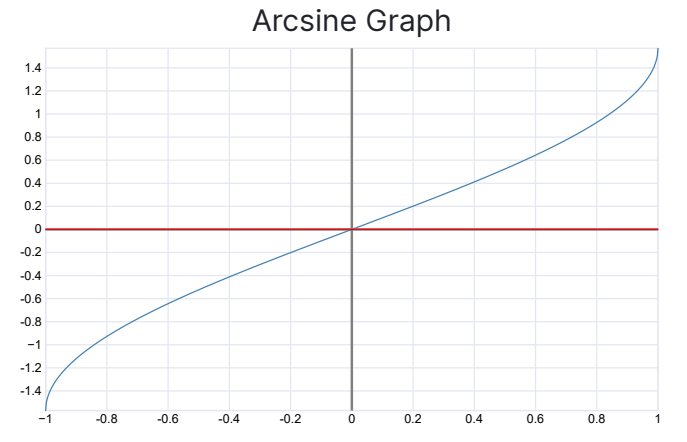
is the inverse of
Definition
The inverse of is the function . Domain: -⇒ Range: is also denoted as
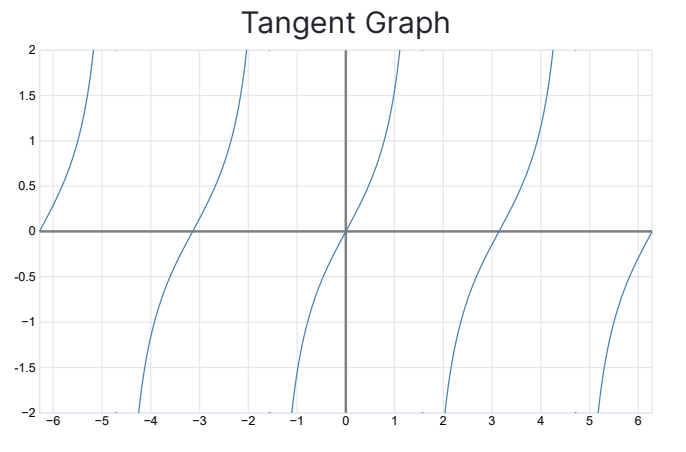
The function has a continuous function that also has asymptotes. The inverse of a tangent function exists on . Keep in mind that we are using parenthesis instead of brackets because the graph that we are looking at does not touch or . Below is a graph of tangent lines.
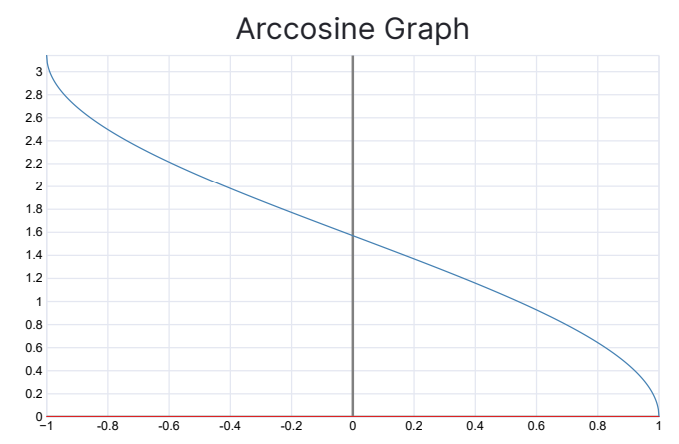
is the inverse of
Definition
The inverse of is the function . Domain: ℝ -⇒ Range: is also denoted as