Table of Contents
- Point Coordinates
- Crystallographic Directions
- Crystallographic Planes
- Determination of Planar (Miller) Indices
- Family of Crystallographic Planes
- Hexagonal Structure
- Linear and Planar Atomic Densities
- Stacking Sequence in FCC and HCP Structures
Point Coordinates
Definition
Fractional multiples of the unit cell edge lengths.
Crystallographic Directions
- Crystallographic Direction: A line between two points, or a vector.
- Any directions parallel to each other are equivalent and have identical indices.
- Specific directions are indicated by square brackets, , and the negative direction is indicated by a bar on top of the corresponding index.
Crystallographic Planes
Any two planes parallel to each other are equivalent and have identical Miller indices.
- If the plane passes the origin, then construct a parallel plane that doesn’t pass the origin, or select a new origin.
- Find the intercepts of the plane along the axes, , , .
- Take reciprocals of the intercepts.
- Convert into smallest integers in the same exact ratio.
- Enclose in parenthesis .
Determination of Planar (Miller) Indices
For cubic crystals (only), planes and directions having the same indices are perpendicular to one another.
Family of Crystallographic Planes
- Several nonparallel planes with different indices are crystallographic equivalent, i.e., a family of crystallographic planes.
- Parenthesis ⇒ Braces
- Caution has to be executed when the lattice is not cubic.
Hexagonal Structure
- Four indices are used instead of 3 indices.
- varies for different structures.
- for hexagonal close-packed (hep) structure.
Linear and Planar Atomic Densities
Stacking Sequence in FCC and HCP Structures
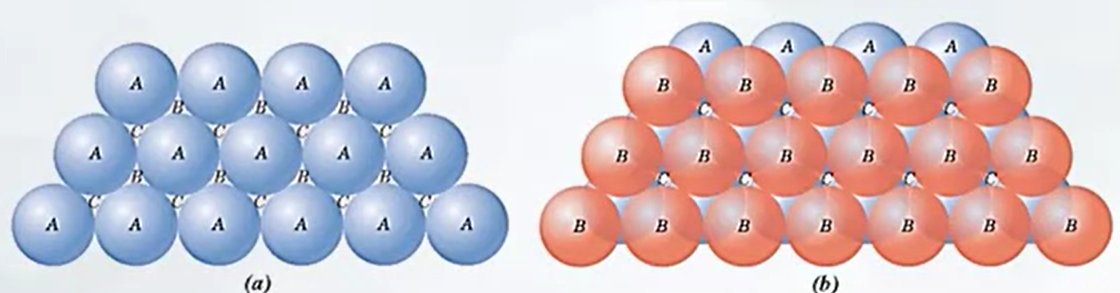
A portion of a close-packed plane of atoms; , , and position are indicated.
The stacking for close-packed atomic planes.
Stacking
- close-packed crystal structure
- close-packed plane of atoms
- FCC
- HEP