Electrical Safety
When electricity is applied to the human body
- Severe burns in the entrance & exit
- Nervous system damaged or destroyed
Fire Safety
- Keep areas around electrical work or equipment clean and free of unnecessary flammable substances.
- Never put electrical wires where they may be walked or run over by other equipment.
- When wires inside a power cord is broken, current is increased, meaning more heat generated than the insulation coatings.
- Repair or replace damaged equipment.
Safety Compressed Gases
- Inspect air hoses for breaks and worn spots. Replace unsafe hoses.
- Make sure there is no leak.
- Maintain in-line oilers in operating condition if they are installed.
- Ensure the system has water sumps installed and drained at regular intervals.
- Filter air that is used for spray painting. (Remove oil & water)
- Never use compressed air to clean hands or clothing. Pressure may be too much force.
- Never spray compressed air near other personnel.
- Straighten, coil, and properly store air hoses when not in use.
- Use tire dollies and other appropriate equipment to mount or remove aircraft tires.
Safety Hazardous Materials
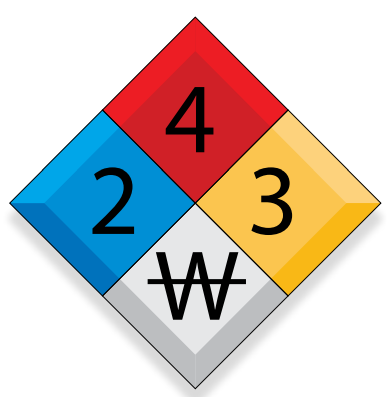
In the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) or also known as the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS), there is a label of a risk diamond. It is a four-color segmented diamond that represents flammability (red), reactivity (yellow), health (blue), and special hazard (white).
- Flammability, Reactivity, & Health: Number from 0 to 4. (0 representing little or no hazard, 4 representing very hazardous)
- Special Hazard: Represented by a word or abbreviation. (e.g. RAD for radiation, ALK for alkali materials, Acid for acidic materials, CARC for carcinogenic materials, and W with a line for high reactivity to water.)
Example of a risk diamond:
Safety Machine Tools
- Wear eye protection.
- Securely clamp all work.
- Set the proper revolutions per minute (RPM) for the material being used.
- Do not allow the spindle to feed beyond its limits of travel.
- Stop the machine before adjusting work or attempting to remove jammed work.
- Clean area when finished.
Flight Line Safety
Hearing Protection
- Always wear hearing protection when available. (May be external or internal)
- Earmuffs/Headphones are external protection.
- Hearing protection that fits into auditory canals are internal protection.
- Essential when working with pneumatic drills, rivet guns, or other loud tools.
FOD
Foreign Object Damage is any damage to the aircraft.
- Never leave tools around intake of a turbine engine.
- Modern gas turbine engine creates low-pressure area in front of the engine, causing any loose objects to be drawn into the engine.
- Exhaust can propel loose objects great distances with enough force to damage anything that is hit.
Safety Around Planes & Helicopters
- Be aware of propellers.
- Never assume the pilot can see you, stay within the pilot’s view while on ramp.
- Turbine engine intakes and exhaust are very hazardous.
- Smoking & open flames are not permitted.
- Be aware of aircraft fluids that can be detrimental to the skin.
- Observe rotor heads and blades to see if they are level. Allow maximum clearance when approaching the helicopter.
- Approach the helicopter in view of pilot.
- Never approach a helicopter carrying anything with vertical height. Can cause blade damage and injury to the individual.
- Never approach single-rotor helicopter from the rear. Tail rotor is invisible when operated.
- Always go around the nose of the helicopter to get to the other side.
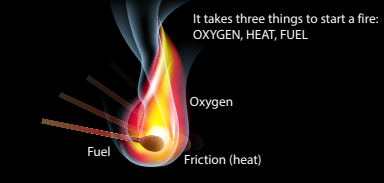
Fire
Reactants:
- Fuel - Combining oxygen, releasing more heat.
- Heat - Accelerates combination of oxygen and fuel, releasing more heat.
- Oxygen - Element that combines chemically with another substance through oxidation. Rapid oxidation is noticed with the release of heat and light, combustion or burning.
Classification
Class A: Involves ordinary combustible materials.
- Wood, cloth, paper, upholstery materials, etc. Class B: Involves flammable petroleum products.
- Combustible liquids, greases, solvents, paints, etc. Class C: Involves energized electrical wiring/equipment.
- Wires, cords, electrical, etc. Class D: Involves metal.
- Flammable metals, etc.
Extinguishers
Carbon Dioxide (): Class A, B, and C
- Never use on Class D fires, water extinguishers can cause explosive expansion on metal. Halogenated Hydrocarbon: Class B and C Carbon Tetrachloride (Halon 104 - ): Toxicity Rating (3)
- Not recommended to be used. Creates hydrochloric acid vapor, chlorine, and phosgene gas, when used on ordinary fires. Methyl Bromide (Halon 1001 - ): Toxicity Rating (2)
- Corrosive to aluminum alloys, magnesium, and zinc.
- Not recommended for aircraft use. Chlorobromomethane (Halon 1011 - ): Toxicity Rating (3)
- Liquefied Gas
- Not recommended for aircraft use. Dibromodifluoromethane (Halon 1202 - ): Toxicity Rating (4)
- Not recommended for aircraft use. Bromochlorodifluoromethane (Halon 1211 - ): Toxicity Rating (5)
- Liquefied Gas
- Colorless, noncorrosive, evaporates rapidly, no residue.
- Does not freeze or cause cold burns, does not harm fabrics, metals, etc.
- Rapidly on fires, producing heavy blanketing mist, eliminating oxygen from fire source. Bromotrifluoromethane (Halon 1301 - ): Toxicity Rating (6)
- Liquefied Gas
- All characteristics of Halon 1211
- Vapor spray, more difficult to direct Dry Powder: Effective on Class B and C, best for Class D
- Varies from gas cartridge charges, stored pressure, force powder out of container.
- Not recommended for aircraft use, except on metal fires.
- Cleanup is difficult, may damage electronic or other delicate equipment.