Interpretation
Info
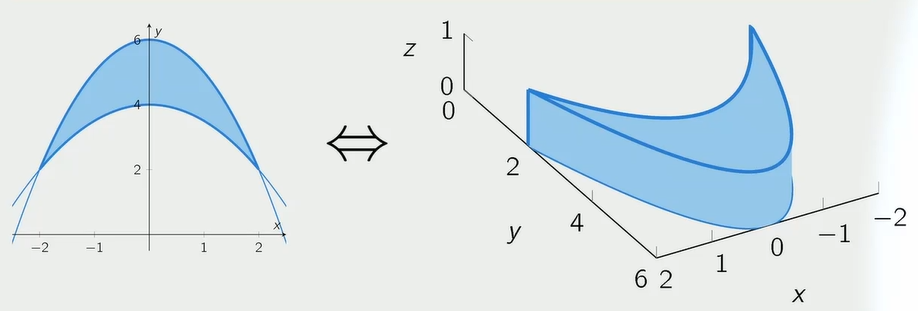
The double integral of over the region D, denoted by
is the (signed) volume under the graph of for in .
Riemann Integral
Definition
The integral of over the rectangle is
if this limit exists.
Theorem
The double integral exists for any continuous function.
Computation Rules (Similar to Single Variable)
Theorem
- If on , then .
Theorem
Theorem
If consists of non-overlapping parts then
In the video the mass and center of mass of a two dimensional object were introduced as important applications of double integrals. Another important application is the so-called moment of inertia of an object that rotates around an axis. This is the amount of torque needed for a desired angular rotation around this axis. For a point mass of mass , the moment of inertia is given by , where is the distance to the rotational axis.
Suppose we now have a plate that occupies a region in the -plane with mass density function , which we rotate around the -axis and we want to compute the moment of inertia, which we denote by . The closest point on the -axis to a given point is of course the point . As such, the square of the distance of the point to the -axis is given by . Therefore, the contribution of a small rectangle with sides and around this point to the total moment of inertia is given by . In order to compute the total moment of inertia around the -axis, we need to add all of these contributions together and we find that
A similar formula holds for the moment of inertia around the -axis, which we denote by , and is given by
Finally, for rotation around the origin, the square of the distance of the point to the origin is given by . So we find that the moment of inertia of rotation around the origin, which we denote by , is given by